Alternatives to long-term care insurance opens the door to a broad spectrum of options for individuals and families seeking solutions for long-term care needs. With the rising costs of traditional insurance and the intricacies involved in long-term care planning, exploring alternatives has become essential for many. This exploration not only highlights the various pathways available but also emphasizes the importance of thoughtful planning to ensure that loved ones receive the care they deserve.
The landscape of long-term care is diverse, comprising various types of services that cater to the unique needs of the elderly. From in-home support and community services to government assistance programs, understanding these alternatives can empower families to make informed decisions without solely relying on insurance policies.
Understanding Long-Term Care
Long-term care (LTC) is an essential component of elderly care, focusing on the support and services needed for individuals who have prolonged illnesses, disabilities, or cognitive impairments. As people age, their healthcare needs often change, making understanding long-term care crucial for families planning for the future. It encompasses a range of services that help individuals with activities of daily living (ADLs) and offers different types of care depending on individual needs.Different types of long-term care are available, each catering to varying levels of assistance required.
These can broadly be categorized into institutional and non-institutional care, providing options that fit both the preferences and needs of seniors.
Types of Long-Term Care
The types of long-term care can be classified based on delivery settings and services provided. Below are the primary categories:
- In-Home Care: Services provided in the individual’s home, including personal care assistance, companionship, and skilled nursing care.
- Assisted Living Facilities: Residential communities that offer support with daily activities while promoting independence for seniors who do not require intensive medical care.
- Nursing Homes: Facilities that provide comprehensive health care and assistance for individuals who need 24-hour medical supervision and support.
- Adult Day Care Services: Programs that provide social activities and care during the day for seniors, allowing caregivers respite while ensuring their loved ones are cared for.
- Memory Care: Specialized care for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia, focusing on safety and cognitive stimulation.
Understanding the financial implications of long-term care is crucial for families as they navigate their options. Long-term care can be expensive, and costs can vary significantly based on the type of care required, geographical location, and duration of services.
“The average cost of a private nursing home in the United States can exceed $100,000 per year.”
Many families may underestimate the financial burden associated with long-term care, making planning and budgeting essential. It is important to evaluate available resources, such as personal savings, government programs, and potential long-term care insurance options, which can help alleviate some of the financial pressure. Being proactive in understanding these aspects can lead to better decision-making and a more secure future for both seniors and their families.
Alternatives to Long-Term Care Insurance

As the need for long-term care continues to grow, many individuals seek alternatives to traditional long-term care insurance. Understanding these alternatives can provide peace of mind and financial security, ensuring that individuals are prepared for future health care needs without the burden of escalating insurance costs.Several alternatives exist, each with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. These include personal savings, government programs, and various financial products designed to offer long-term care solutions.
Exploring these options can help individuals make informed decisions about their future care needs.
Use of Personal Savings
Personal savings are often considered a viable alternative to long-term care insurance. This approach allows individuals to have direct control over their funds, using them as needed for long-term care expenses. Benefits of using personal savings include:
- Flexibility: Individuals can allocate funds as they see fit, whether for in-home care, assisted living, or nursing facilities.
- No Premiums: There are no ongoing insurance premiums to worry about, which can free up budget space for other expenses.
- Control Over Funds: Individuals maintain control over their savings, ensuring they can use the money for other purposes if their care needs change.
However, there are also drawbacks:
- Risk of Depletion: Personal savings may not be sufficient if care is needed for an extended period, leading to financial strain.
- Investment Growth Potential: Funds allocated for future care might miss out on potential growth if they are kept in low-interest accounts.
- Emotional Stress: The burden of paying directly for care can lead to stress and anxiety as expenses accumulate.
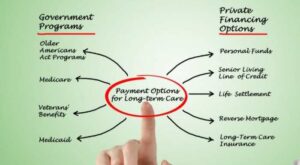
Government Programs for Long-Term Care
Government programs play a crucial role in providing alternatives to long-term care insurance. These programs may offer various forms of assistance to individuals needing care.Key government programs include:
- Medicaid: This state and federal program helps with medical costs for individuals with limited income and resources, covering certain long-term care services.
- Veterans Benefits: Eligible veterans may receive benefits that cover long-term care services through programs like the VA Aid and Attendance benefit.
- State-Specific Programs: Many states have their own programs that provide funding or support for home care services, adult day care, and other long-term care alternatives.
These government programs can significantly alleviate the financial burden of long-term care. However, they may come with eligibility requirements and application processes that can be complex and time-consuming.
Understanding the intricacies of personal savings and government programs can empower individuals to make sound decisions regarding their long-term care needs.
Planning for Long-Term Care Needs
Planning for long-term care is an essential part of preparing for the future, especially as individuals grow older or face health challenges. Understanding and evaluating care needs can help ensure that appropriate options are available when the time comes. This guide aims to assist individuals in assessing their long-term care needs, providing essential tools and considerations for effective planning.Assessing long-term care needs involves evaluating personal health, lifestyle, and preferences.
Individuals should consider factors such as current health status, potential future health issues, and the level of care required. Other considerations include the ability to perform daily activities, the availability of family support, and financial resources. This comprehensive evaluation lays the groundwork for making informed choices regarding long-term care options.
Guide for Assessing Long-Term Care Needs
Creating a solid plan for long-term care starts with a thorough assessment of individual needs. This guide Artikels key aspects to consider:
- Current Health Status: Review existing medical conditions and treatments. Understanding chronic illnesses can help anticipate future care requirements.
- Daily Living Activities: Evaluate the ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) such as bathing, dressing, eating, and mobility.
- Cognitive Function: Consider cognitive abilities and any potential decline that may affect decision-making or self-care.
- Support System: Assess the availability of family, friends, or community resources that can assist in care provision.
- Financial Resources: Examine personal finances, including savings, income sources, and insurance coverage that may affect care options.
Checklist for Evaluating Long-Term Care Options
Having a checklist can significantly streamline the process of evaluating long-term care options. It ensures that individuals consider all relevant factors before making decisions. Below is a checklist that includes both insurance and non-insurance solutions:
- Type of Care Needed: Determine whether in-home care, assisted living, or skilled nursing facility care is necessary.
- Cost Considerations: Analyze the costs associated with different care options and compare them to available financial resources.
- Location Preference: Decide on preferred locations for care, whether at home, in a community, or closer to family.
- Quality of Care: Research and evaluate reviews, ratings, and accreditations of potential care providers.
- Flexibility: Consider whether the care option allows for changes in care level as health needs evolve over time.
- Family Involvement: Assess how the chosen care option accommodates family participation in care decisions and support.
Importance of Family Involvement in Long-Term Care Planning
Family members play a crucial role in long-term care planning. Their involvement can ensure that the care plan aligns with the individual’s preferences and values. By engaging family members in discussions about care needs, individuals can benefit from their insights and support.Family involvement fosters open communication and facilitates decisions regarding care options. The support network can help with logistics, provide emotional support, and even assist in daily care tasks.
Involving family also ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding expectations and responsibilities.
“Effective long-term care planning is not just about health; it’s about ensuring that personal values and family support are integrated into every step.”
Final Conclusion

In summary, navigating the realm of long-term care requires a comprehensive understanding of the available alternatives to long-term care insurance. By evaluating personal savings, government options, and community resources, families can craft a tailored approach to their care needs. Ultimately, proactive planning and family involvement play a crucial role in ensuring that older adults receive the appropriate support, fostering peace of mind for everyone involved.
Q&A
What are the most common alternatives to long-term care insurance?
Common alternatives include personal savings, home equity, Medicaid, and community-based support services.
How can personal savings be effectively used for long-term care?
Families can set aside funds in designated savings accounts or utilize investment vehicles specifically meant for future care expenses.
Are there government programs that assist with long-term care costs?
Yes, programs like Medicaid and the Veterans Administration offer assistance for eligible individuals needing long-term care services.
How important is family involvement in long-term care planning?
Family involvement is crucial as it ensures that care preferences are understood and that support systems are put in place to meet the needs of the individual.
Can community resources provide sufficient long-term care support?
Yes, many communities offer resources such as meal delivery services, transportation, and in-home care that can significantly aid in long-term care.